Note that GitLab doesn't always show you changes from all users. It likes to default the commits listing to just your commits. Try switching to the branches page and then back to the commits page to see if you see changes from everybody or just you. If you cannot see all changes, you will reset back to the wrong commit.
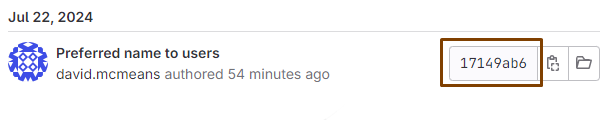
Find the commit you want to be the new latest, or HEAD, commit. Get it's commit ID. Note that this means all commits after this one will be removed.
Make sure the local repository is update to with the website repository.
In the local repo, enter
git reset --hard commitID
where commitID is like 17149ab6
You will see
HEAD is now at 17149ab Preferred name to users
Then
git push -f origin main
If you are not sure about the names of your branches, look for a response like Your branch is up to date with 'origin/main'. You might have Your branch is up to date with 'origin/master. If so you would use
git push -f origin master
You might get
remote: GitLab: You are not allowed to force push code to a protected branch on this project.
If so, you will have to unprotect the branch in the GitLab website. Good idea to to re-protect it once you are done.
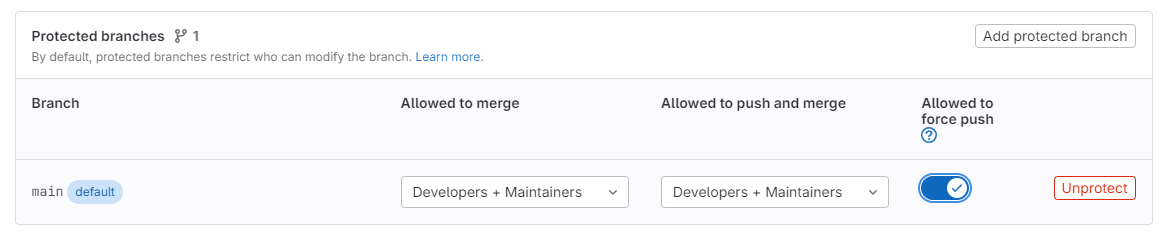
Note, you might just be able to toggle the force push setting without having to remove the branch protection altogether.
Once the force push works, refresh the repository commits page on the website. You should see all commits that occurred after the commitID you specified are no longer present.
If you have multiple commits you want to remove, it is not a bad idea to try this for each commit so you can prove that its working they way you expect.
Helpful commands
git log main where main is the branch name. This will list all the recent commits. Use 'q' to exit the listing.
git show --name-only commitHash to show the files changed in a commit.
Read more articles
- Log in to post comments
